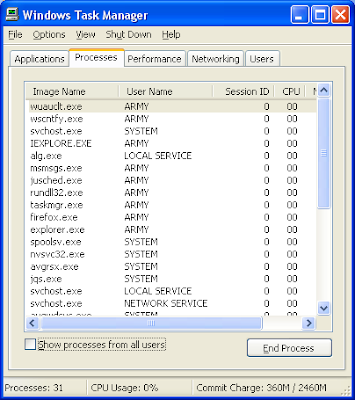
The Windows Task Manager provides information about the computer's performance and displays details about programs and processes running on the computer, especially those that are running in the background. You can end programs or processes, start programs, and view a dynamic display of the computer's performance by using the Windows Task Manager. It can also be used to shut down or restart the computer as well as going to stand by mode.
With the Windows Task Manager, you can also determine if which processes is taking too much of the computer's resources. You will also be able to determine if which programs that are automatically starting. More importantly, you can see through the Windows Task Manager if there is a virus or spyware that is running on the computer.
Another very good use of the Windows Task Manager is to forcefully quit a software that froze, which is similar to the Force Quit feature of the Macintosh OS X computer.
Also, make sure that you know the process that you are trying to close from the Windows Task Manager because it can shut down your computer if you closed a process that you should not be closing, especially those processes that are categorized as SYSTEM under the "User Name" column of the PROCESSES tab.
The common way to invoke the Windows Task Manager is by pressing the CTRL and ALT keys on the keyboard at the same time, and while pressing them, press the DELETE key, then the Windows Task Manager will appear.
The Windows Task Manager can be disabled on Windows XP Home Edition as well as on the Windows XP Professional. Therefore, if it was disabled, you will get the message "Task Manager has been disabled by your administrator." It is possible that the owner of the computer disabled the Windows Task Manager or your computer already got infected by a virus or spyware and it disabled the Windows Task Manager so that you will not be able to quit it and for it to run free on your system.
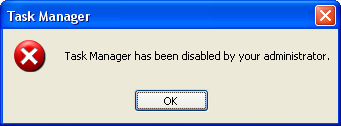
Fear not because you can enable back the Windows Task Manager. Here are the steps to enable the Windows Task Manager on Windows XP. Enabling the Windows Task Manager through the Group Policy is to actually disabling it there, so don't be confused.
1. Click the START button and choose RUN.
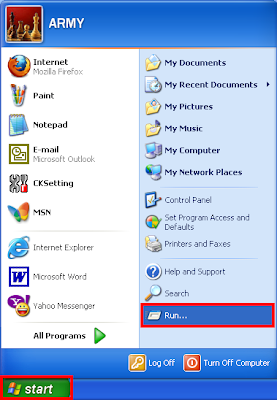
2. Type GPEDIT.MSC into the Run box and hist the ENTER key on the keyboard.
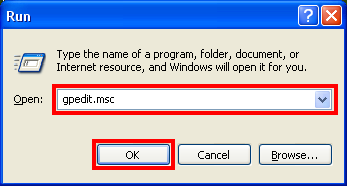
3. Expand the USER CONFIGURATION category.
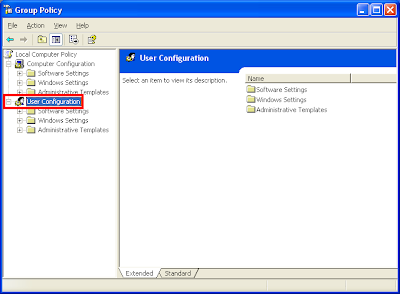
4. Expand the ADMINISTRATIVE TEMPLATES category.
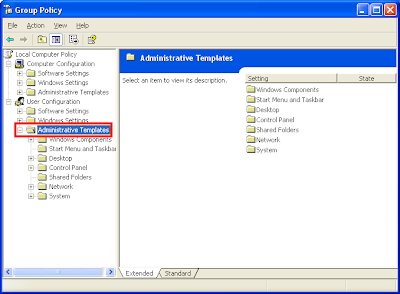
5. Expand the SYSTEM category.
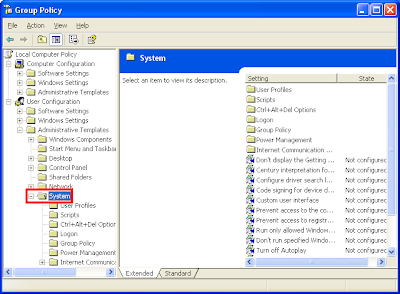
6. Click the CTRL+ALT+DEL OPTION category.
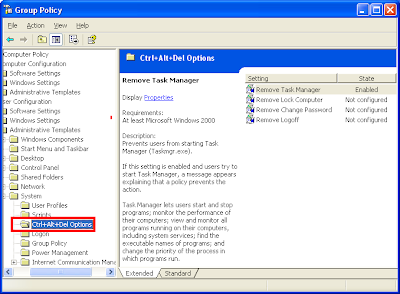
7. Right-click on REMOVE TASK MANAGER option and choose PROPERTIES.
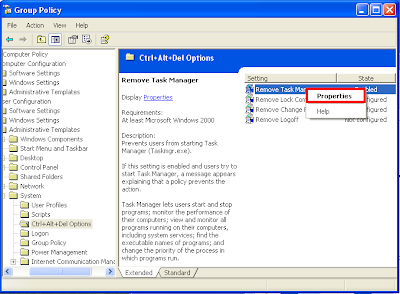
8. Mark the ENABLED option.
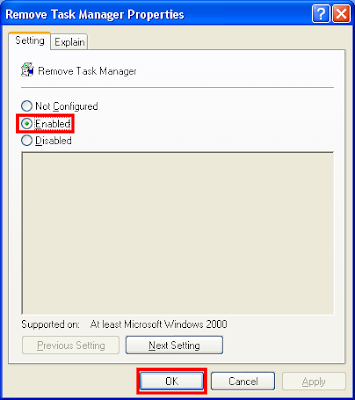
9. Click OK button.
Another way to enable or disable the Windows Task Manager is by doing the following steps:
1. Click the START button and choose RUN.
2. Type REGEDIT into the Run box and hist the ENTER key on the keyboard.
3. Search for HKEY_CURRENT_USER.
4. Expand the SOFTWARE category.
5. Expand the MICROSOFT category.
6. Expand the WINDOWS category.
7. Expand the CURRENTVERSION category.
8. Expand the POLICIES category
9. Expand the SYSTEM category.
10. Right-click on DisableTaskMgr option and choose MODIFY.
11. Value: 1 - Enable this key (disables TaskManager)
Value: 0 - Disable (enables TaskManager)
12. Click OK button.
You can now open the Windows Task Manager by pressing the CTRL+ALT+DELETE keys on the keyboard.
NOTE: If you still cannot enable the Windows Task Manager, it is most likely that your computer got infected by a virus or spyware.
NOTE: Networked computers that under a group policy will not be able to enable the Windows Task Manager.
With the Windows Task Manager, you can also determine if which processes is taking too much of the computer's resources. You will also be able to determine if which programs that are automatically starting. More importantly, you can see through the Windows Task Manager if there is a virus or spyware that is running on the computer.
Another very good use of the Windows Task Manager is to forcefully quit a software that froze, which is similar to the Force Quit feature of the Macintosh OS X computer.
Also, make sure that you know the process that you are trying to close from the Windows Task Manager because it can shut down your computer if you closed a process that you should not be closing, especially those processes that are categorized as SYSTEM under the "User Name" column of the PROCESSES tab.
The common way to invoke the Windows Task Manager is by pressing the CTRL and ALT keys on the keyboard at the same time, and while pressing them, press the DELETE key, then the Windows Task Manager will appear.
The Windows Task Manager can be disabled on Windows XP Home Edition as well as on the Windows XP Professional. Therefore, if it was disabled, you will get the message "Task Manager has been disabled by your administrator." It is possible that the owner of the computer disabled the Windows Task Manager or your computer already got infected by a virus or spyware and it disabled the Windows Task Manager so that you will not be able to quit it and for it to run free on your system.

Fear not because you can enable back the Windows Task Manager. Here are the steps to enable the Windows Task Manager on Windows XP. Enabling the Windows Task Manager through the Group Policy is to actually disabling it there, so don't be confused.
1. Click the START button and choose RUN.

2. Type GPEDIT.MSC into the Run box and hist the ENTER key on the keyboard.

3. Expand the USER CONFIGURATION category.

4. Expand the ADMINISTRATIVE TEMPLATES category.

5. Expand the SYSTEM category.

6. Click the CTRL+ALT+DEL OPTION category.

7. Right-click on REMOVE TASK MANAGER option and choose PROPERTIES.

8. Mark the ENABLED option.

9. Click OK button.
Another way to enable or disable the Windows Task Manager is by doing the following steps:
1. Click the START button and choose RUN.
2. Type REGEDIT into the Run box and hist the ENTER key on the keyboard.
3. Search for HKEY_CURRENT_USER.
4. Expand the SOFTWARE category.
5. Expand the MICROSOFT category.
6. Expand the WINDOWS category.
7. Expand the CURRENTVERSION category.
8. Expand the POLICIES category
9. Expand the SYSTEM category.
10. Right-click on DisableTaskMgr option and choose MODIFY.
11. Value: 1 - Enable this key (disables TaskManager)
Value: 0 - Disable (enables TaskManager)
12. Click OK button.
You can now open the Windows Task Manager by pressing the CTRL+ALT+DELETE keys on the keyboard.

NOTE: If you still cannot enable the Windows Task Manager, it is most likely that your computer got infected by a virus or spyware.
NOTE: Networked computers that under a group policy will not be able to enable the Windows Task Manager.
No comments:
Post a Comment